Hello again to another Hacking Intro Tutorial. Last entry we discussed basic network terminology and concepts. For this tutorial we will dive into Aircrack-Ng, an amazing hacking software that we will be using for many of our Wi-Fi hacks.
An important thing to note, is that Aircrack-Ng(The ng standing for New Generation), is not just a single tool, but a a suite of tools within Kali Linux. Within this suite there is Aircrack, which is used to crack passwords. Although, before we get into that, we will need to familiar ourselves with the tools in this suite.
Getting Started
First thing first, we need to make sure your adapter is recognized by Kali Linux. You will need to open the Kali Linux terminal and type in
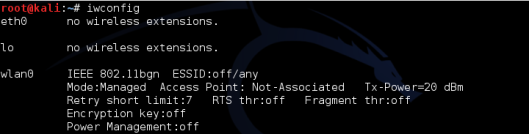
root@kali: ~# iwconfig
As you can see, my adapter is recognized and tells me it’s capable of 802.11bgn. It Also tells me the ESSID is off, and other information regarding the adapter.
Airmon-Ng
Say you are at your local coffee shop trying to access a webpage on your laptop using the public Wi-Fi. Normally people would think that when you want to load your webpage you are directly requesting this information from the router.
However, your computer doesn’t directly send data anywhere. Instead, your computer broadcasts data in packets with its destination in the header. Every node in the network (or switch) receives this packet, and determines whether or not if it’s the intended recipient. If not, it will choose to ignore it.
For example, let’s say you want to go on Google.com. Your laptop will shout this request by saying, “I need Google.com!”. Most of the nodes on the network will simply ignore this request. This request to Google.com will keep being passed around until Google.com receives it. This will then be indexed to your router, which then responds back with “I can give you Google.com!”. The response is once again ignored by every node that isn’t yours.
If we switch our adapter to promiscuous mode, all network traffic will be received by us, intended or not. To start this, we will want to type in airmon-ng, the action (start), and the interface (wlan0).
root@kali: ~# airmon-ng start wlan0
This returns with key information about the chipset and driver. Also keep note that the designation has changed from wlan0 to mon0.
Airodump-Ng
Airdump-Ng is another tool useful in password cracking. Enabling this will allow us to capture packet that we specify. If you type the following into the terminal:
root@kali: ~# airodump-ng mon0
You will see a list of all APs, their BSSID(Mac Address), their power, beacon frames, the channel speed, number of data packets, speed, encryption method, cipher type used, authentication method, and ESSID within range.
Aireplay-Ng
Another powerful tool in the Aircrack-Ng suite. This tool is able to accelerate or generate traffic on an AP. This can be useful for performing hacks such as: WEP and WPA2 password cracks, bumping people off their access point, and APR injection.
Airdecap-Ng
This tool will allow us to decrypt network traffic once we have cracked the key. With this, we can not only use the bandwidth on the AP, but also be able to see what everyone connected to the AP is doing.
Airolab-Ng
Airolab-Ng allows us to store or mange ESSID’s (The name of the AP), and password list to help speed up cracking WEP and WPA2 networks.
Airbase-Ng
This tool is a very useful tool that we will cover more of in a later tutorial. With this we can perform “Evil Twin” attacks.
Aircrack-Ng
Our last tool is Aircrack-Ng. This is the primary application in the tool suite. We can use this for password cracking and dictionary attacks for WEP and WPA2 networks.
That is it for the tools in the AirCrack-Ng suite. While there are more tools in this suite, we will primarily be focusing on these ones for our tutorials. For the next entry, we will explore Evil Twin attacks and how you can do one.


Pingback: Hacking Intro Tutorial V: Ceating An Evil Twin | Gravie